Data breaches are more costly than ever, averaging USD 4.88 million in 2024—a 10% rise. This spike is largely due to increased expenses related to lost business, operational downtime, and higher regulatory fines.
The latest Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024 by IBM and the Ponemon Institute offers a reality check on these rising costs, with insights that go beyond numbers. For organizations aiming to keep up with today’s cyber threat landscape, the report’s key takeaways reveal where to prioritize resources, how to improve response strategies, and why investments in staffing, automation, and proactive security measures are essential.
Whether looking to stay secure into 2025 or assessing today’s budget allocation, companies can benefit from understanding the trends driving these costs and what steps can be taken to manage breach risks more effectively. Here’s what we’ve learned…
The average cost of a data breach jumped to USD 4.88 million from USD 4.45 million in 2023, a 10% spike and the highest increase since the pandemic. » – Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024
Security Staffing Shortages: A Growing Challenge
Security staffing shortages are a growing challenge, leading to higher breach costs. Over half of the organizations reported severe shortages—a 26.2% increase from last year. High-level skill shortages drove average breach costs up to USD 5.74 million, compared to USD 3.98 million for those less affected by skill gaps.
The Impact of Shadow Data
Shadow data—unmanaged or unmonitored data stored across various environments—was implicated in 35% of breaches in 2024. Breaches involving data across multiple environments took longer to identify and contain, raising costs. As you rely more on cloud infrastructure, your attack surface expands, so it’s crucial that you actively monitor and protect these environments. Breaches linked to shadow data accounted for 40% of incidents, with data stored in public clouds being the most vulnerable (25%), followed by on-premises (20%) and private clouds (15%).
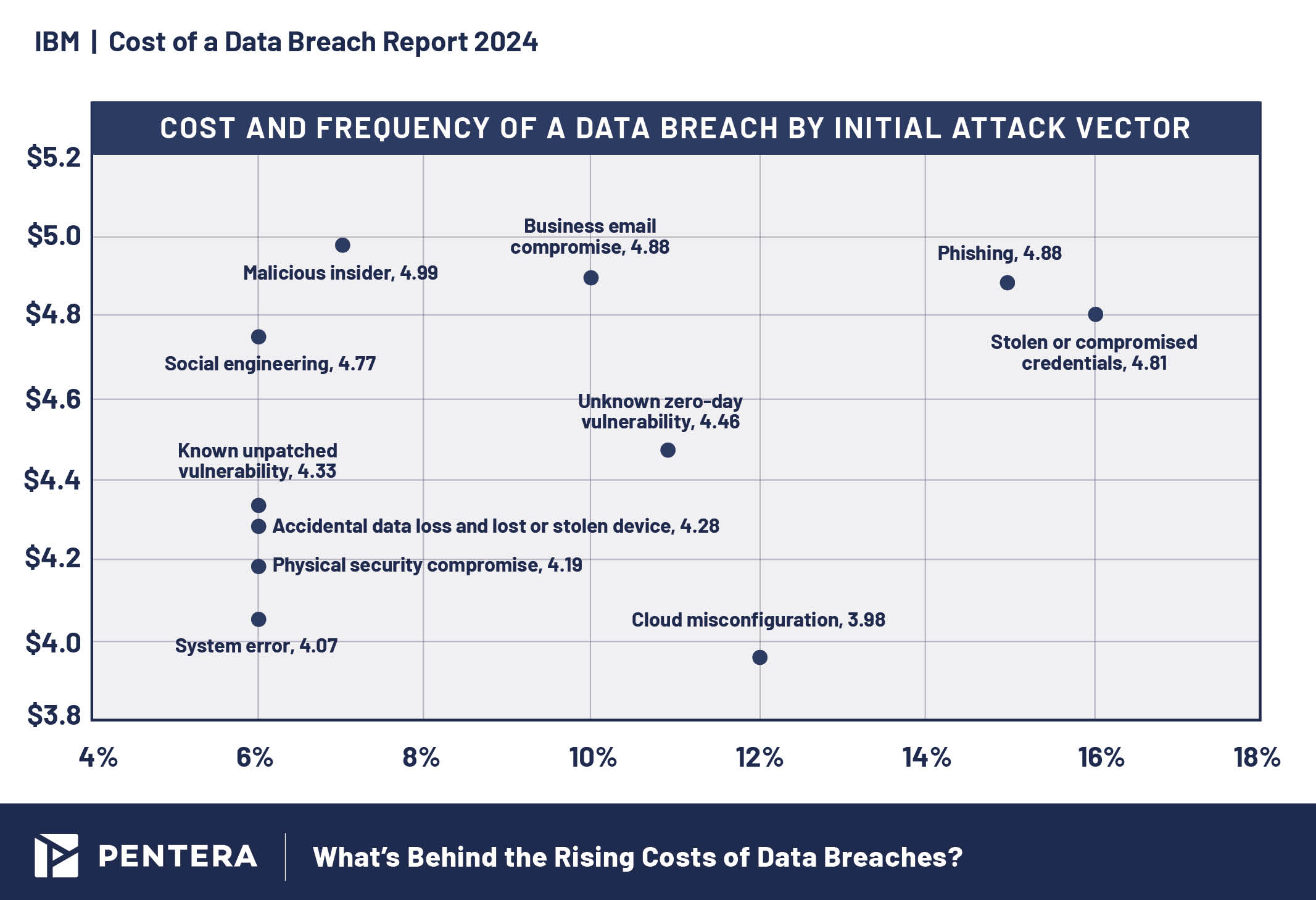
Cost and Frequency of Breaches by Attack Vector
Phishing and compromised credentials remain the most common attack vectors, accounting for a significant portion of breaches. Compromised credentials were involved in 16% of breaches, costing an average of USD 4.81 million. Phishing came in a close second, at 15% of attack vectors, but with a higher cost, at USD 4.88 million per breach. Malicious insider attacks were the most expensive, averaging USD 4.99 million, though they accounted for only 7% of breaches.
Cost and frequency of breaches by attack vector, 2024.
The Importance of Proactive Breach Identification
How you identify a breach significantly impacts the associated costs. Breaches achieved by attackers cost an average of USD 5.53 million, whereas those detected by the organization’s security team were less costly, at USD 4.55 million. Improving internal detection is essential to reducing breach costs and minimizing the damage to your organization. The report also noted that security teams identified breaches 42% of the time, an improvement from one-third of the time in the previous year.
The Cost of Breaches by Data Type
Customer Personal Identifiable Information (PII) was the most frequently compromised data type in 2024, involved in 46% of breaches. The average per-record cost of PII increased to USD 173, reflecting the significant financial impact of protecting sensitive customer information. Intellectual Property (IP) records were also heavily targeted, involved in 43% of breaches.
Costs associated with breaches involving PII and IP data types in 2024.
The Impact of Extortion Attacks
Extortion attacks, including ransomware, have proven to be especially costly. In 2024, destructive attacks reached an average cost of USD 5.68 million, more expensive than traditional ransomware or data exfiltration incidents. Notably, organizations that involved law enforcement during these attacks were able to reduce breach costs by nearly USD 1 million, proving the value of collaborating with authorities.
Breaches Involving Compromised Credentials
Breaches involving stolen or compromised credentials took the longest time to identify and contain, averaging 292 days—longer than any other attack vector. Similar attacks that exploited employee access, such as phishing and social engineering, also had extended durations, with phishing attacks lasting an average of 261 days and social engineering attacks taking 257 days. Additionally, attacks using zero-day vulnerabilities were among the most time-consuming to contain.
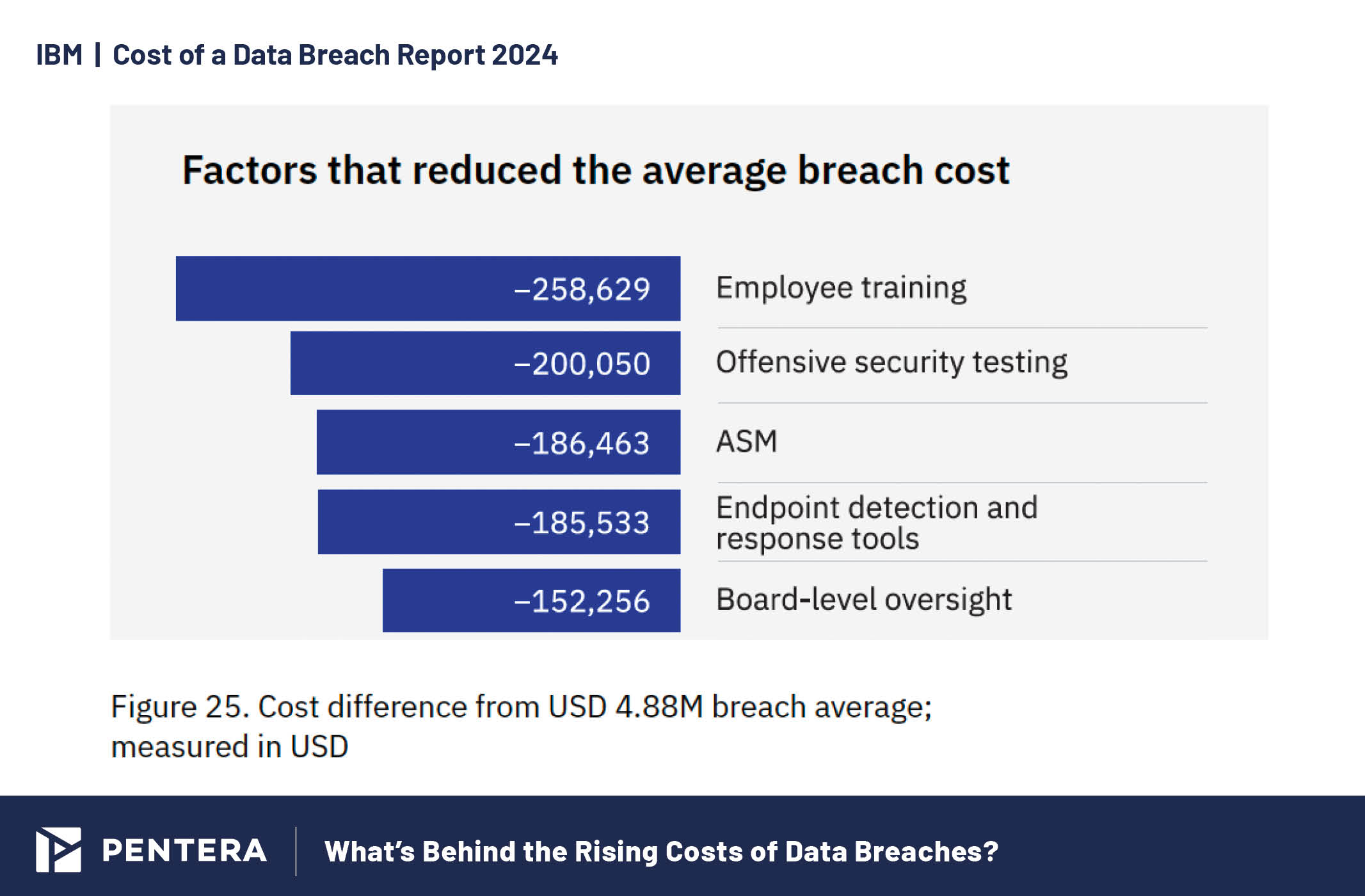
Key factors that helped reduce breach costs in 2024.
Breach Recovery Time
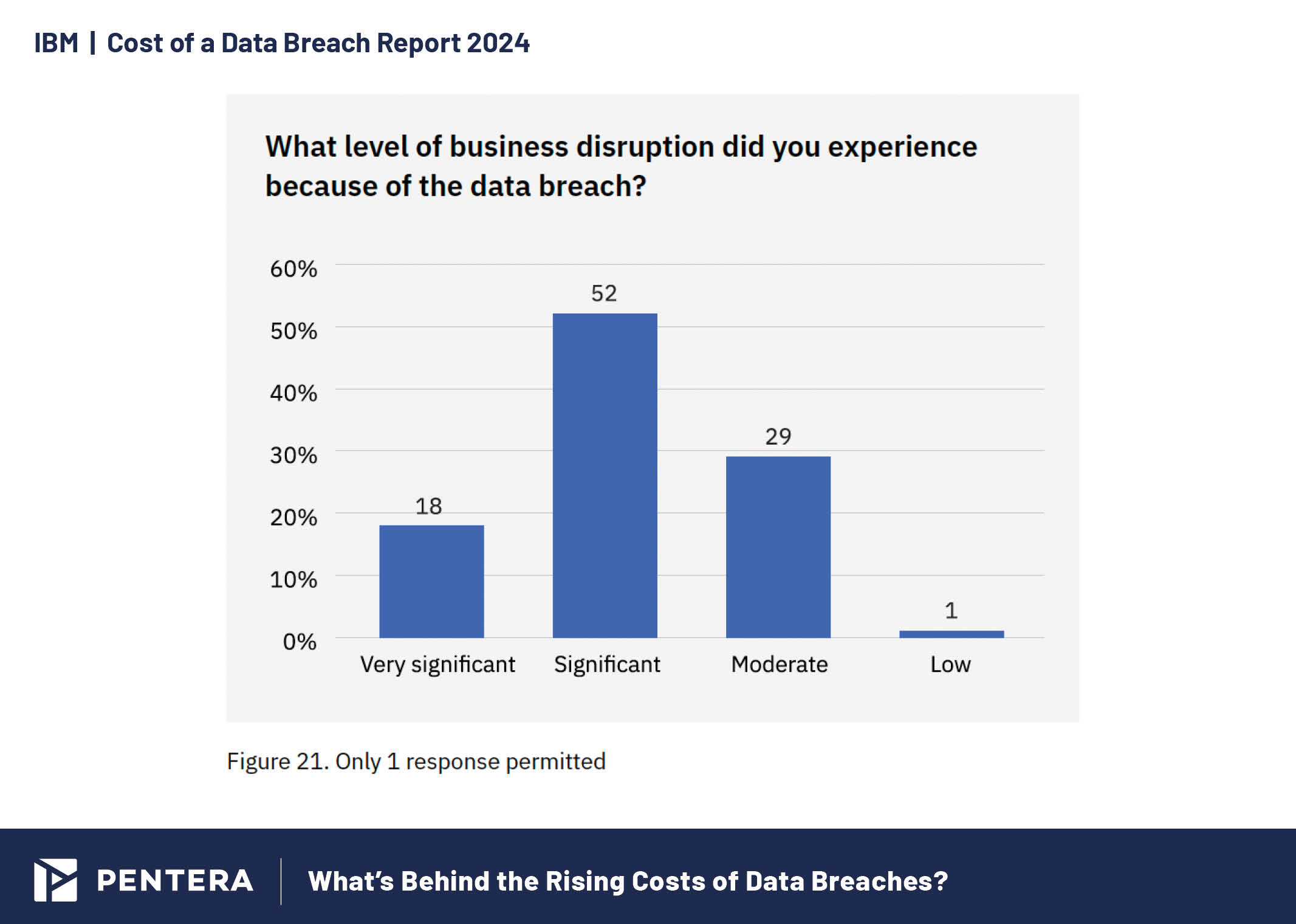
The mean time to identify and contain a breach decreased to 258 days, the lowest in seven years. However, only 12% of organizations reported full recovery from their breaches, with most still working on their remediation efforts. Of the organizations that fully recovered, most took over 100 days, highlighting the lasting impact of breaches.
Levels of business disruption caused by data breaches in 2024.
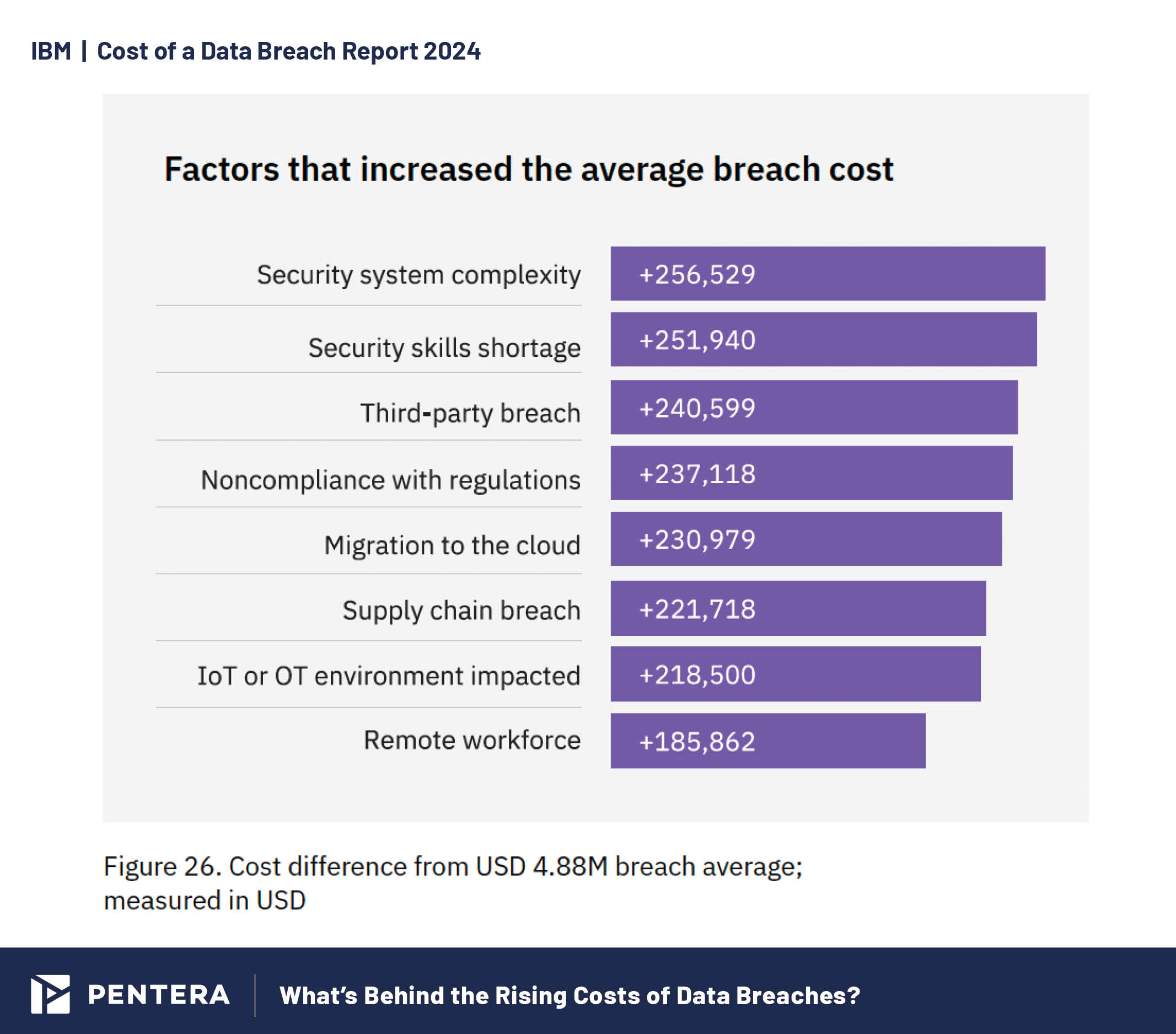
High Levels of Security System Complexity and Third-Party Breaches
Complex security systems, skill shortages, and third-party breaches are significant contributors to increased breach costs. The more complex your security infrastructure, the more challenging it becomes to manage and protect effectively, often leading to vulnerabilities that can be exploited. When combined with a shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, these factors create a perfect storm. All this underscores the necessity of continuous security validation to help control these risks, and reduce the likelihood of a breach, and the resulting financial impact.
The Role of AI and Automation in Cost Reduction
Organizations leveraging AI and automation in security workflows see notable cost reductions. Those integrating AI into attack surface management and posture management processes typically lower breach costs, highlighting the value of these advanced security solutions.
« When (AI is) deployed extensively across prevention workflows—attack surface management (ASM), red-teaming and posture management—organizations averaged USD 2.2 million less in breach costs compared to those with no AI use in prevention workflows. » – Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024
Strategic Security Investments for 2025
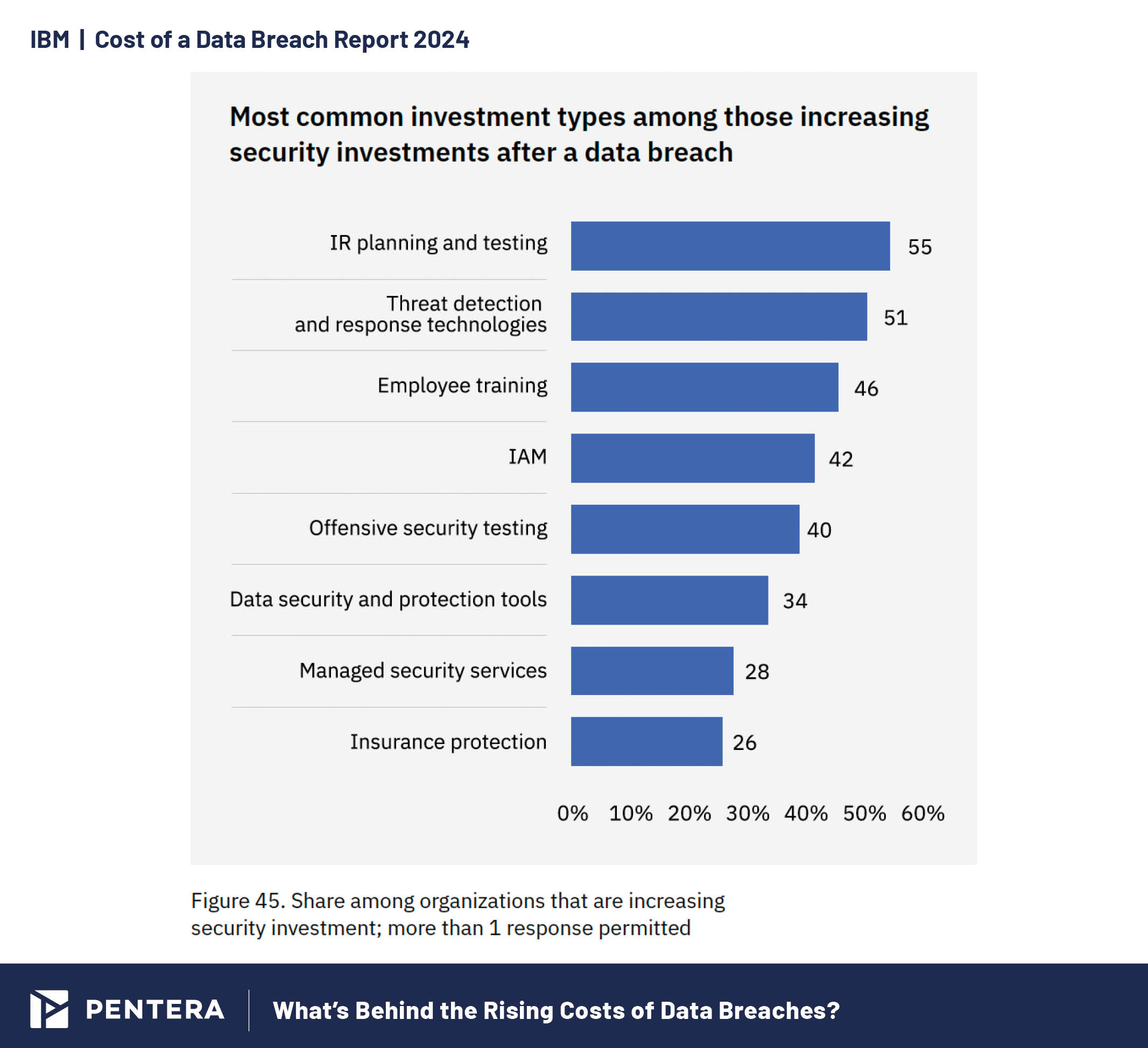
As 2025 approaches, trends show a strong emphasis on managing breaches and reducing their impact, with a mix of reactive and proactive approaches. According to the report, organizations are focusing on key areas to strengthen defenses: 55% are prioritizing Incident Response (IR) planning and testing, with 51% investing in threat detection and response technologies, 46% enhancing employee training, and 42% focusing on Identity and Access Management (IAM).
Strategic security investments post-breach in 2024.
With attack surfaces expanding across hybrid environments, continuous security validation and a balanced mix of proactive and reactive defenses will help organizations to avoid the full blow of a breach. Preparing for these trends now will set companies up for a stronger, more cost-effective year ahead.
For more industry statistics on how security leaders manage pentesting, click here to read the full Pentera State of Pentesting Report 2024.