What is vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is a risk-based cybersecurity approach by which organizations proactively protect their digital infrastructure against breaches. It comprises the identification, assessment, and remediation of security vulnerabilities in computer systems, applications, and networks in order to prevent cyber attacks and limit potential damage should one take place.
Vulnerability Management is a continuous process that involves identifying, evaluating, prioritizing, and addressing vulnerabilities across all digital assets. Key components include Vulnerability Assessment, Zero Trust, and Risk Prioritization to strengthen security posture.
Understanding vulnerability management
Vulnerability management exists as a method for organizations to deal with the challenges of having an expansive IT environment.
Large organizations typically rely on a diverse and continually expanding array of digital assets in their operations including servers, cloud applications, third-party software, physical routers and endpoint devices, and more. Relying on an extensive IT infrastructure opens up a wide variety of possible entry points for attackers, so organizations utilize vulnerability management as a means of proactively managing cybersecurity risks.
By its nature, vulnerability management is cyclical and serves to continuously strengthen security posture. To this end, it encompasses the following key processes:
- Asset identification: Organizational assets must be discovered and subsequently cataloged so that they can be managed on an ongoing basis.
- Vulnerability scanning and prioritization: Assets are assessed to identify vulnerabilities and gauge risk levels so that they can be prioritized for remediation.
- Mitigation: Once identified and prioritized, security gaps are remediated through updates, patch management, and configuration management to prevent exploitation.
- Validation: When security gaps have been remediated, systems are retested to validate the effectiveness of newly implemented measures.
- Monitoring and reporting: Organizational assets are continuously monitored and reported on so that further vulnerabilities can be swiftly addressed.
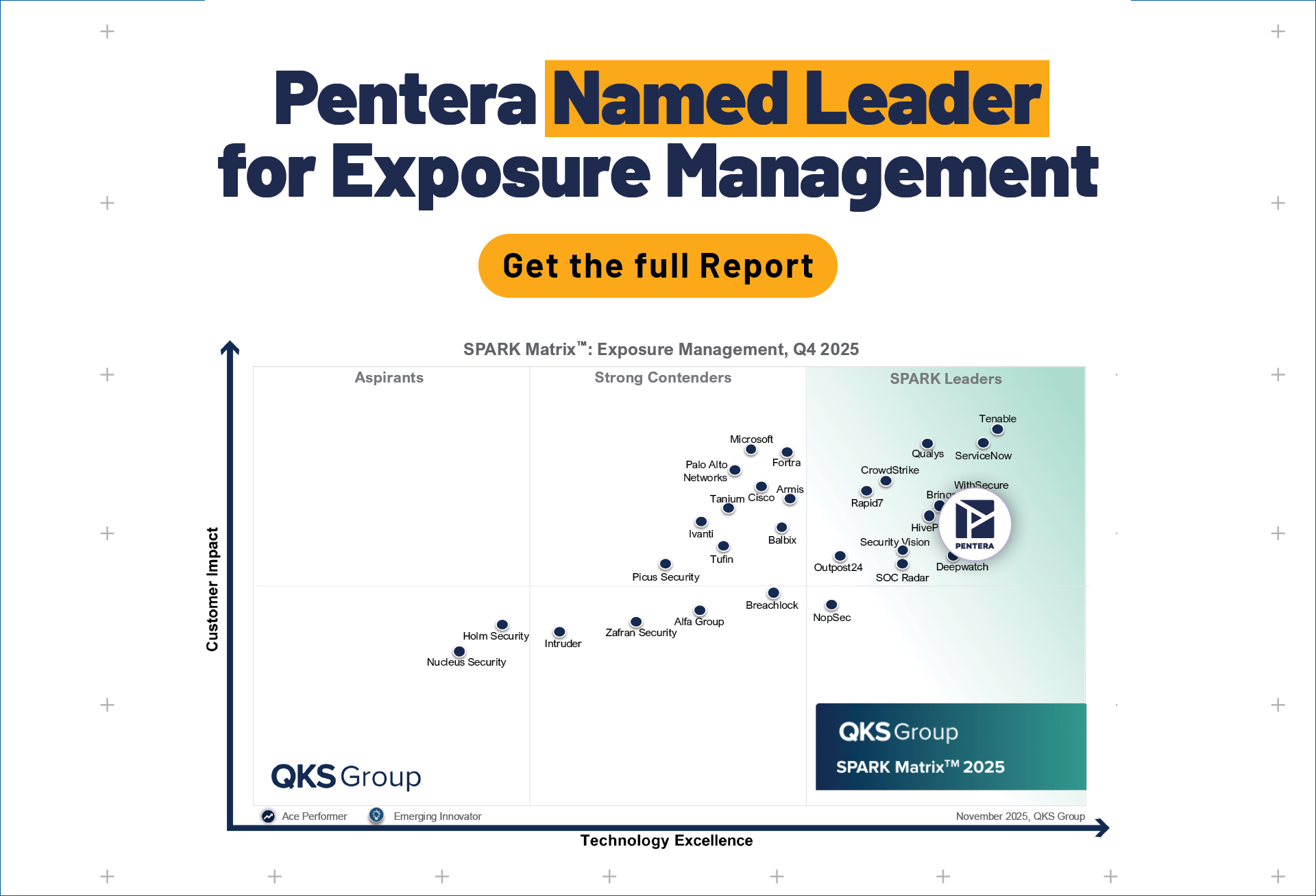
Introduction to the Gartner Magic Quadrant
The Gartner Magic Quadrant is a system by which Gartner, a leading IT research and consulting firm, provides visual representations of data relating to the direction, maturity, and participants of certain markets.
Gartner’s Magic Quadrant shows the relative market positions of vendors using two primary metrics: completeness of vision and ability to execute. These are represented on the graph by the x-axis and y-axis, respectively, with both axes bisecting the graph to create four quadrants. Gartner evaluates vendors using its standard criteria and represents each in one of the four quadrants, denoting their place in the market as niche players, challengers, visionaries, or leaders.
The Gartner Magic Quadrant for vulnerability management
The Magic Quadrant for vulnerability management indicates some key trends in the market. In particular, it shows that organizations engaging in vulnerability management are increasingly choosing to use solutions that combine vulnerability assessments with other cybersecurity functionalities so that they can proactively assess, manage, and report on risks posed by security vulnerabilities. As a result, enterprises providing agentless security validation products, such as Pentera, are becoming increasingly dominant in the market due to the wider utility of their solutions.
Benefits of using the Gartner Magic Quadrant
By distilling extensive research into a snapshot of the current state of a market, the Gartner Magic Quadrant offers several key benefits to organizations, including the following:
- Informed decision-making: By comparing vendors with the Magic Quadrant, organizations can make informed decisions on products and services to align with their needs.
- Improved vendor relationships: The Magic Quadrant offers a common reference framework for clients and vendors, enabling organizations to more clearly establish their expectations with product or service vendors.
- Reduced business risk: As the Magic Quadrant gives an indicator of vendor performance and reputation, it helps organizations to determine the long-term viability of a particular solution.
Managing cybersecurity risk with vulnerability management
In an increasingly digital world, organizations everywhere are relying on increasingly expansive and intricate IT infrastructures, and this elevates potential cybersecurity risks. As such, vulnerability management should be considered a core part of a thoughtful and modern cybersecurity approach. By providing organizations with a means of identifying and remediating points of exposure as they appear, vulnerability is key to a strong security posture.
Frequently asked questions
What is vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is a cybersecurity approach by which organizations continuously monitor, assess, and remediate vulnerabilities in their IT infrastructures to strengthen their security posture.
Why is vulnerability management important?
Vulnerability management is important because it empowers organizations to act pre-emptively in detecting and remediating cybersecurity vulnerabilities. As such, it allows them to protect themselves against cyber threats by staying one step ahead of would-be attackers.
What is the process of vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management involves the following key processes: asset discovery, vulnerability scanning, prioritization, remediation, validation, and continuous monitoring. As Vulnerability management is cyclical, these processes are repeated continuously to ensure that security posture is strengthened regularly.
What happens if critical vulnerabilities are discovered during vulnerability management?
If critical vulnerabilities are discovered during vulnerability management, they are assessed and prioritized based on their associated risk level. They are then swiftly remediated, and newly implemented security measures are validated to ensure that the vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed.
Can I request a summary of vulnerability management results or reports?
Yes, you can request a summer of vulnerability management results or reports. These summaries offer detailed information on your organization’s security posture, highlighting points of exposure and offering recommended actions for remediation and risk mitigation.
Identify and prioritize vulnerabilities effectively.
Review impact of proven attack paths to identify your riskiest security gaps.