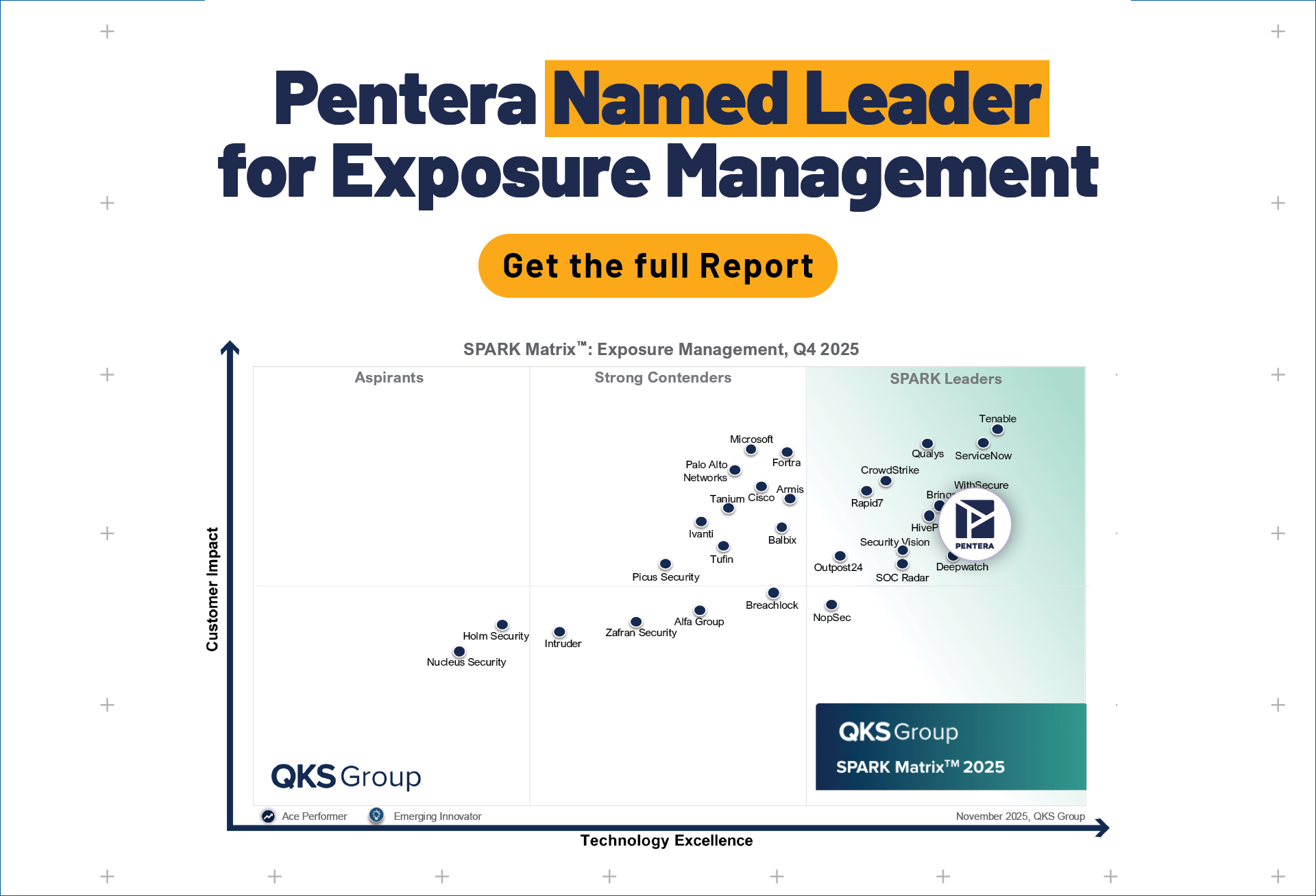
What is Continuous Security Validation?
Continuous Security Validation (CSV) is a proactive and ongoing approach to security validation. It involves ongoing validation and testing of an organization’s security measures through the implementation of automated security validation tools. CSV enables security teams to continuously evaluate the effectiveness of their security controls and identify vulnerabilities.
In Security Validation, Continuous Validation offers ongoing assessments to ensure resilience, adapting to new threats and ensuring security controls are consistently effective.
Why is Continuous Security Validation important?
Continuous Security Validation is important because it enables organizations to ensure that their security measures are fit for purpose in an evolving threat landscape. Unlike traditional periodic testing methods, CSV facilitates the real-time detection of threats so that they can be promptly remediated to prevent exploitation. With CSV, organizations can proactively address weaknesses to bolster their security posture and ensure that security measures are up-to-date and in compliance with industry regulations and standards. This continuous approach facilitates both stronger defenses and rapid incident response to effectively minimize business risk.
What are the benefits and challenges of Continuous Security Validation?
Like every security approach, there are benefits and challenges to be aware of with regard to Continuous Security Validation:
Benefits
- Real-time insight for remediation: Continuous Security Validation enables security teams to gather up-to-date information on security vulnerabilities to enable prompt remediation.
- Improved security posture: Continuously validating the effectiveness of security measures can guide security teams as they iterate upon security measures for better protection.
- Enhanced incident response: By simulating real-world tactics to validate security measures, CSV can enable security teams to detect and respond to threats more effectively.
- Resource efficiency: CSV automates validation processes, so it reduces the expenses associated with manual testing through vendors.
- Regulatory compliance: By continuously validating security controls through CSV, organizations can ensure that their security measures are fit for purpose and always adhere to regulatory standards.
Challenges
- Integration: Integrating automated validation tools into an existing security framework can be a complex and resource-intensive process. Additionally, some workflows may require the assistance of skilled third parties if suitably skilled personnel aren’t available within an organization.
- False positives/negatives: CSV leverages automated tools, which may generate false positives or negatives, necessitating manual intervention from security teams at some stages of the validation process.
- Updating: In order to ensure efficacy and regulatory compliance, validation tools need to be regularly updated to ensure that they account for emerging vulnerabilities and attack vectors.
What are the methods of Continuous Security Validation?
There are a range of different testing methods which comprise the CSV process. These include the following:
- Automated penetration testing: CSV leverages automated penetration testing, simulating real-world attack techniques to identify vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems and networks.
- Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS): CSV continuously assesses the effectiveness of security controls by simulating various specific cyberattack scenarios.
- Vulnerability scanning: Validation tools conduct regularly vulnerability scans of systems, networks, and applications so that potential security weaknesses can be identified and reported.
- Configuration management: Validation tools check system configurations to assess whether they align with security standards.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): CSV emphasizes the real-time monitoring and analysis of security events to facilitate better threat detection and response.
What to do with the findings of Continuous Security Validation?
When vulnerabilities are identified through CSV, security teams should seek to prioritize and remediate them promptly with security updates, software patches, systems reconfigurations, and the adjustment of security policies, where necessary. Findings and remediation efforts should also be clearly documented, and follow-up assessments conducted to ensure that identified vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed.
Embracing CSV for continuous improvement in security
Continuous Security Validation is an essential component of a proactive, preventative security approach. By continuously assessing security measures and providing security teams with real-time information, CSV enables organizations to enhance their defenses and increase readiness. In doing so, they can protect their assets and effectively mitigate risk in an evolving threat landscape.
FAQs
What are the tools for Continuous Security Validation?
There are a range of tools used in Continuous Security Validation, including automated penetration testing tools, Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS) tools, configuration management tools, vulnerability scanners, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems.
What types of tests are commonly included in Continuous Security Validation?
Common test types included in Continuous Security Validation include automated penetration testing, breach and attack simulations, vulnerability scanning, configuration checks, and real-time security event monitoring.
Is Continuous Security Validation suitable for all types of software projects?
Yes. Since CSV leverages automated tools, it is highly adaptable and scalable, meaning it can be utilized across a wide variety of software projects.
How to take the findings from CSV to the next level?
To gain maximal value from the findings of CSV, organizations must seek to integrate results into a wider security strategy that focuses on prioritized remediation and continuous updating and improvement. This way, the information gathered through CSV can inform effective risk management, empowering organizations to protect essential assets and maintain operational continuity.
Identify cloud vulnerabilities.
Detect and address vulnerabilities in your cloud environment.